Advanced Urine Drug Testing
NOAH Clinical Laboratory utilizes the latest technology available to detect a wide array of drugs and metabolites in urine samples. We employ modern LC-MS/MS instrumentation to provide results in the quickest, most accurate fashion possible. Use of confirmatory quantitation methods provide many benefits when compared to point-of-care (POC) testing and screening assays.
Download PDFApplications of toxicology testing include:
Benefits of Quantitative Confirmation Analysis with LC-MS/MS
Drug Screen Limitations
Lack Specificity
Drug classes vs. individual drugs
Opiates vs 6-monoacetylmorphine (heroin metabolite)
Cross Reactivity
High concentrations of other drugs can yield false positives
DRI Methadone EIA false positive with Tapentadol and metabolites
Lack Sensitivity
Cutoffs typically lower
Opiate cutoff = 300 ng/mL vs 50 ng/mL
Not Comprehensive
Covers approx. 20 drug classes and without focus on metabolites
Detection of noroxycodone (oxycodone metabolite) would indicate biological metabolism, not spiking of oxycodone into the sample
Semi-quantitative at best
Interpretation of a Positive Drug Screen
- Patient is compliant and took the prescription as directed
- Patient added drug to the urine after collection
- Patient took one dose prior to collection
- Patient took another drug which cross- reacts with the test, i.e. a false-positive
Pseudoephedrine can give a “Positive” result for an amphetamine screening test
Interpretation of a Negative Drug Screen
- Patient is not compliant
- Patient did not follow dosing regimen
- Less frequent or lower dose
- Drug present but below the cutoff
- Dilute or adulterated urine
- False-negative
- Test does not react with drug of interest
- Appropriately targeted test may not be available
- Altered pharmacokinetic variables
- Ultra-fast metabolizer – no parent drug present, only me tabolite
- Poor drug absorption
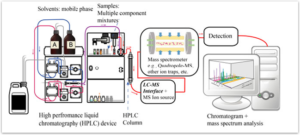
Strengths of LC-MS/MS Analysis
High specificity
Can differentiate between individual drugs
No cross reactivity
Utilizes 3 unique analyte properties to ID
Increased sensitivity
– Cutoffs are lower than immunoassay techniques
– Reduced false negatives
Comprehensive
– Can detect many individual compounds with respective metabolites
– Current capability is 75 analytes
Quantitative
Use of certified reference materials allow accurate quantitative values

